What is Ophthalmology?
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and diseases of the eyeball and orbit.
About Eye
Eyes is the pair of globular organs of sight in human head.
Eye is a complex optical system which collects light from surrounding, regulates its intensity through diaphragm (Iris), focuses through lens and form an image. Converts this image into electric signals and transmit these signals to the brain.
Structure of EYE
- EYE BALL – Ball shaped structure of approx. 1 inch diameter.
- ORBIT – Cone shaped bony cavity in the skull enclosing the eyeball.
- FATTY TISSUE – protects and supports the eyeball within the orbit.
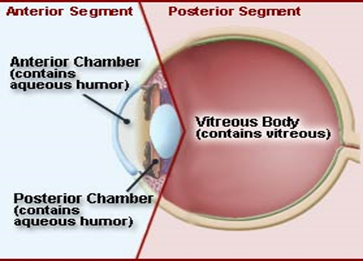
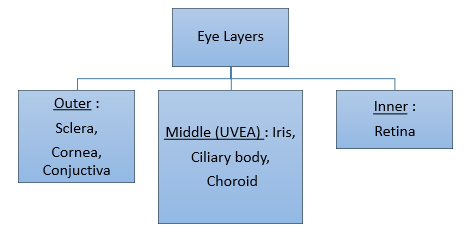
Outer Layer:
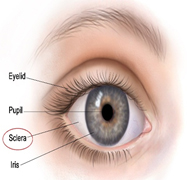
- Sclera :
White part of the eye is called Sclera.
It forms the supporting wall of the eyeball.
It is connected with 6 muscles which hold the eyeball.
- Conjuctiva:
A thin, clear, moist membrane that coats the inner surfaces of the eyelids (palpebral conjunctiva) and the outer surface of the eye (ocular, or bulbar, conjunctiva).
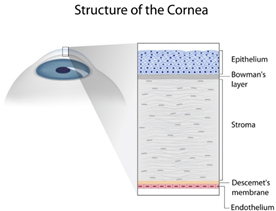
- Cornea:
Front portion of the eyeball, Avascular, Transparent, Provides most of the eye’s optical power, Primary function is to refract light.
Middle Layer:
- Iris:
Thin circular structure in the eye responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil, and thus amount of light reaching the retina.
Eye color is defined by Iris color.
In optical term – Iris is the diaphragm of eye and Pupil is aperture of eye
- Ciliary Body
An extension of choroid containing muscles, blood vessels and secretory cells.
Function:
- Hold the lens and controls lens shape.
- Control ciliary epithelium which produces Aqueous Humour.
- Provides oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues
- CHOROID:
The choroid is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the white of the eye and retina (at the back of the eye). It is part of the uvea and supplies nutrients to the inner parts of the eye.
Inner Layer – RETINA
Third and inner coat of the eye which is light sensitive layer of tissue.
Retina captures all the light rays, process them into nerve impulse which is send to brain via optic nerve.
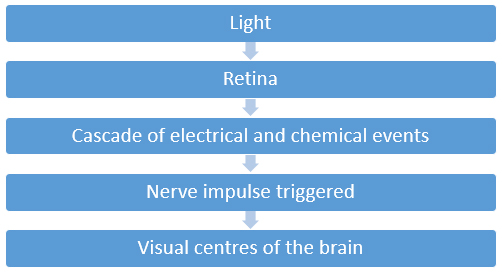
- Retina is a layered structure with neurons.
- Those neurons which are photosensitive are called Photoreceptor cells.
- These photoreceptor cells are called RODS and CONES

Retina-Macula :
Area of Central Vision
Sharpest image formation
Contains Predominantly Cones Cells
Central part of macula is called Fovea. Fovea is the area of sharpest image formation.
PUPIL
Pupil is a hole located in the center of the Iris that allows light to strike the retina.
It is just like aperture of Camera to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
In bright light Pupil contracts or become narrower, and in dim light pupil expands or become wider
LENS
Lens are transparent, biconvex structure in the eye that along with cornea helps to refract light to be focused on retina.
The lens by changing shape adjust focal distance of eye. So that sharp clear image form on retina of the object at various distances
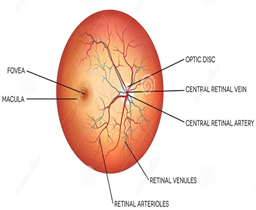
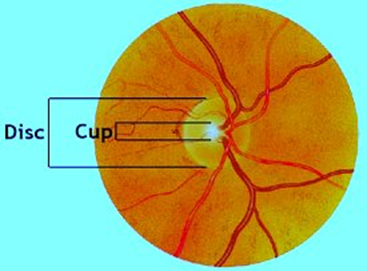
OPTIC DISC
The circular part on retina which is not sensitive to light is called Optic Disc.
- If the cupfills 1/10 of the disc, the ratio will be 0.1. If it fills 7/10 of the disc, the ratio is 0.7.
- The normal cup-to-disc ratiois 0.3.
A large cup-to-disc ratio may imply glaucoma or other pathology.
OCULAR MUSCLES